The cannabis industry stands at a fascinating crossroads of agriculture, technology, and regulatory evolution. As legalization spreads across North America and beyond, cultivators face mounting pressure to maximize yields, ensure product consistency, and meet stringent quality standards—all while navigating complex compliance requirements. Enter artificial intelligence: a transformative force reshaping how cannabis is grown, monitored, and brought to market.
Key Takeaways:
- AI turns cannabis farming into a precise, data-driven process
- Sensors and machine learning optimize climate, water, and nutrients
- Computer vision detects pests, diseases, and harvest timing early
- Predictive analytics prevent problems before they impact crops
- AI reduces water, energy use, and operational costs
- Breeding and genetics improve faster with AI insights
- Compliance and quality control become more efficient
- The best results come from combining AI with grower expertise
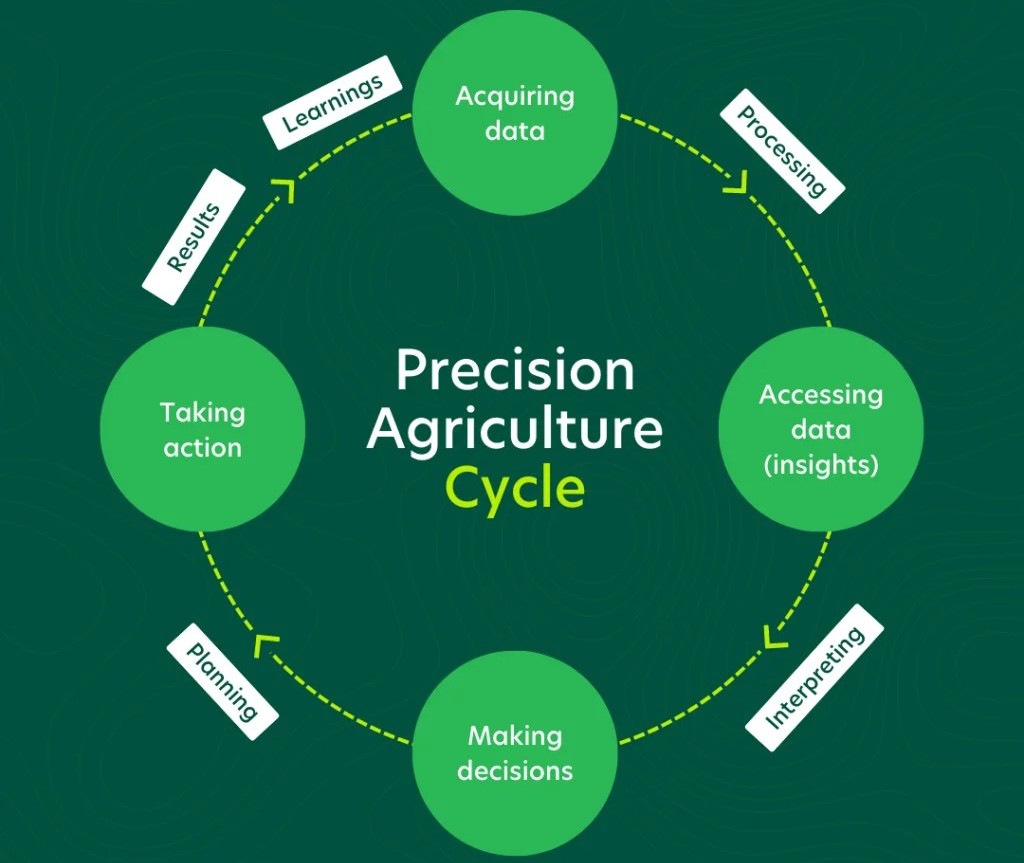
Precision Growing: AI as the Ultimate Cultivator
At the heart of AI-driven cannabis farming lies precision agriculture—the practice of optimizing inputs and interventions at the individual plant level. Modern grow facilities increasingly deploy networks of sensors that continuously monitor dozens of environmental parameters. These sensors track everything from soil moisture and pH levels to ambient CO2 concentrations and leaf surface temperature.
What transforms this data from mere numbers into actionable intelligence is machine learning. AI algorithms analyze patterns across millions of data points, learning to recognize the subtle signatures that precede problems or signal optimal growing windows. For instance, an AI system might detect that a specific combination of temperature, humidity, and light intensity consistently produces higher trichome density in a particular strain. It can then automatically adjust environmental controls to maintain these ideal conditions.
Climate control represents one of the most impactful applications. Traditional HVAC systems operate on simple feedback loops—if temperature exceeds a threshold, cooling activates. AI-powered systems think several steps ahead, using predictive models to anticipate environmental changes before they occur. By analyzing historical patterns, weather forecasts, and real-time sensor data, these systems can preemptively adjust climate controls, maintaining remarkably stable conditions while reducing energy consumption by up to thirty percent.
Water management similarly benefits from AI optimization. Cannabis plants require precise irrigation—too little water stunts growth, while overwatering invites root diseases and nutrient lockout. AI-driven irrigation systems consider not just soil moisture but also plant growth stage, ambient conditions, and strain-specific requirements. Some advanced systems even incorporate computer vision, analyzing leaf curl and coloration to detect early signs of water stress invisible to the human eye.
Computer Vision: Teaching Machines to See Like Master Growers
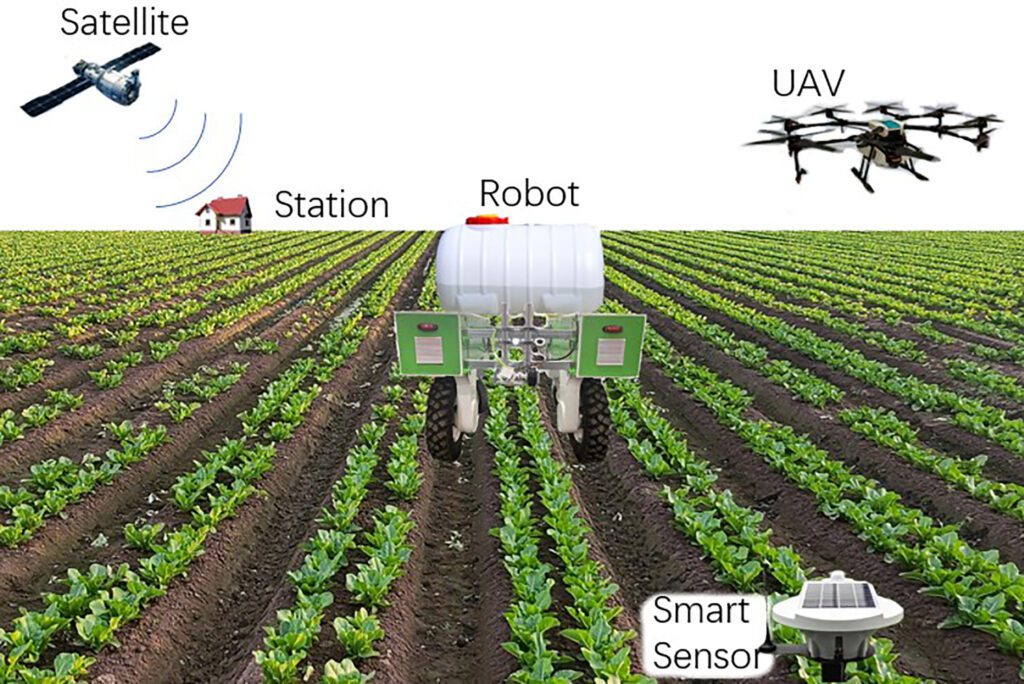
Perhaps no AI technology has proven more transformative than computer vision. High resolution cameras now monitor plants continuously, with deep learning algorithms trained to recognize everything from pest infestations to nutrient deficiencies to optimal harvest timing.
Early disease detection showcases the power of this approach. Fungal infections like powdery mildew or botrytis can devastate entire crops if left unchecked, yet early-stage infections are often difficult to spot until significant damage occurs. Computer vision systems trained on thousands of images can identify the subtle discolorations and texture changes that signal infection days before human observers notice anything amiss. This early warning enables targeted interventions that contain problems before they spread, dramatically reducing crop losses and minimizing pesticide use.
Phenotype tracking represents another compelling application. Cannabis genetics vary enormously, even among plants from the same seed batch. Computer vision systems can monitor individual plant characteristics—height, branching pattern, flower density, leaf structure—building detailed phenotypic profiles. Cultivators use this data to identify superior specimens for breeding programs or to detect plants that deviate from desired specifications.
Harvest timing optimization may be where computer vision delivers the most immediate value. Determining peak harvest windows requires assessing trichome maturity, which traditionally meant sampling flowers and examining them under magnification. AI powered systems now perform this assessment continuously and non-destructively, analyzing trichome color and morphology across entire plants. Some systems even predict cannabinoid and terpene profiles based on visual cues, helping growers time harvests for specific chemical compositions.
Predictive Analytics: From Reactive to Proactive Farming
The transition from reactive problem-solving to proactive management represents AI’s most profound impact on cannabis cultivation. Traditional growing involves responding to issues as they arise—adjusting nutrients when deficiencies appear, treating pests after detection, modifying environments when plants show stress. AI enables a fundamentally different approach.
Predictive models trained on historical growing data can forecast problems before they manifest. An AI system might recognize that current environmental trends mirror conditions that previously led to calcium deficiency, prompting preemptive nutrient adjustments. Or it might predict that an approaching weather pattern will likely trigger increased transpiration, automatically increasing irrigation frequency before plants experience stress.
Yield prediction has become remarkably sophisticated. By analyzing plant growth rates, environmental conditions, and historical harvest data, AI models can forecast final yields weeks before harvest with impressive accuracy. This foresight enables better planning for processing capacity, labor allocation, and market timing. Some cultivators report that AI driven yield predictions now outperform estimates from experienced master growers, particularly when dealing with new strains or environmental conditions.
Energy optimization through predictive analytics deserves special mention, as energy costs represent a major expense for indoor cultivation. AI systems analyze electricity pricing, weather patterns, and plant requirements to schedule energy-intensive operations during off-peak hours when rates are lowest. They might delay lighting cycles slightly or adjust HVAC setpoints within acceptable ranges to shift consumption away from peak rate periods, achieving substantial cost savings without compromising plant health.
Integrated Pest Management: Smarter Defenses
Cannabis pests—from spider mites to aphids to fungus gnats—pose constant threats to crop health. Traditional pest management often relies on scheduled preventive applications or reactive treatments after problems are spotted. AI brings unprecedented sophistication to integrated pest management strategies.
Environmental monitoring systems now predict pest pressure based on conditions. Certain temperature and humidity ranges favor specific pests, and AI models trained on historical infestation data can alert growers when conditions become conducive to outbreaks. This enables precisely timed preventive measures, applying treatments only when actually needed rather than on arbitrary schedules.
Some facilities deploy AI-controlled biocontrol systems. Rather than chemical pesticides, these operations use beneficial insects that prey on common cannabis pests. AI systems monitor pest populations through automated trapping and counting, releasing predators in optimal numbers and locations. This biological approach, guided by real-time data and predictive models, often proves more effective and sustainable than chemical interventions.
Computer vision surveillance represents the cutting edge of pest detection. Networks of cameras continuously scan plants, with AI algorithms trained to recognize pest damage patterns, egg clusters, or the pests themselves. When detection occurs, the system immediately alerts staff and can even trigger localized responses like activating sticky traps or adjusting environmental conditions in affected zones. Early reports suggest such systems can reduce crop losses from pests by more than half compared to traditional monitoring methods.

Genetics and Breeding: Accelerating Strain Development
Cannabis breeding traditionally required years of careful crosses, grow-outs, and selection. AI dramatically accelerates this process by identifying promising genetic combinations and predicting offspring characteristics before seeds are even planted.
Genomic analysis powered by machine learning helps breeders understand the complex genetic architecture underlying desirable traits. Cannabis genetics are notoriously intricate, with cannabinoid production, terpene profiles, growth patterns, and disease resistance controlled by networks of interacting genes. AI algorithms can analyze genetic sequences alongside phenotypic data from thousands of plants, mapping correlations between specific genetic markers and observable characteristics.
This enables predictive breeding, where cultivators can estimate the likely properties of crosses before investing time and resources in growing them out. Want a strain with specific THC and CBD ratios, particular terpene profiles, and resistance to powdery mildew? AI can analyze parent genetics and suggest crosses most likely to produce the desired combination, dramatically improving the odds of success.
Phenotype prediction from seedling stage represents another breakthrough. By analyzing genetic data, early growth patterns, and even seedling images, AI models can predict mature plant characteristics with surprising accuracy. This allows breeders to cull unlikely candidates early, focusing resources on the most promising specimens and shortening breeding cycles from years to months.
Supply Chain and Market Intelligence
AI’s impact extends beyond the grow room into business operations and market strategy. Demand forecasting models analyze sales data, seasonal patterns, regulatory changes, and broader market trends to predict demand for specific products. This intelligence helps cultivators decide which strains to grow, in what quantities, and when to bring them to market.
Inventory management becomes vastly more sophisticated with AI assistance. Cannabis products have defined shelf lives, and regulatory requirements demand precise tracking. AI systems optimize inventory levels, minimizing waste from expired products while ensuring sufficient stock to meet demand. They can even suggest product bundling strategies or promotional timing based on inventory levels and predicted demand.
Price optimization represents a particularly valuable application in competitive markets. AI algorithms analyze competitor pricing, product quality metrics, market demand, and regulatory factors to recommend optimal pricing strategies. Some systems even implement dynamic pricing, adjusting rates in response to real-time market conditions while respecting regulatory constraints.

Challenges and Considerations
Despite its tremendous promise, AI adoption in cannabis cultivation faces real challenges. Initial implementation costs can be substantial, particularly for smaller operations. While prices for sensors, cameras, and computing power continue declining, outfitting a facility with comprehensive monitoring and control systems still represents significant capital investment.
Data quality issues plague early implementations. Machine learning models are only as good as their training data, and the relative youth of legal cannabis markets means historical datasets are often limited or inconsistent. Cultivators who operated in gray markets before legalization may lack systematic records, while newer operations haven’t accumulated enough data for robust model training.
Regulatory uncertainty complicates technology adoption. Cannabis regulations vary dramatically across jurisdictions and continue evolving. AI systems designed for compliance in one market may not translate to others, and rapid regulatory changes can quickly render expensive systems obsolete or require costly reprogramming.
The human element remains crucial. AI should augment rather than replace experienced growers, yet achieving this balance proves challenging in practice. Some cultivators report that staff resist AI recommendations, trusting their intuition over algorithmic suggestions. Others struggle with over-reliance on automation, allowing skills to atrophy or missing problems that fall outside AI detection parameters.
The Road Ahead
The next frontier in cannabis AI involves integration and interoperability. Currently, many facilities deploy multiple disconnected systems—separate platforms for climate control, irrigation, pest monitoring, and business management. The future points toward unified ecosystems where these systems communicate seamlessly, sharing data and coordinating actions for holistic optimization.
Edge computing and on-device AI will likely become standard, processing data locally rather than relying on cloud connectivity. This approach offers faster response times, better reliability, and enhanced data security—all important considerations for commercial cultivators.
Personalization represents an intriguing possibility. Imagine AI systems that learn individual growers’ preferences and decision-making patterns, adapting their recommendations to align with each cultivator’s philosophy and risk tolerance. Rather than one-size-fits-all optimization, these systems would become true collaborators, extending human judgment rather than overriding it.
As datasets grow and algorithms improve, we may see AI-driven innovation in areas we can barely imagine today. Automated breeding programs that continuously evolve new varieties. Robotic systems that handle everything from transplanting to trimming. Virtual reality interfaces that allow growers to “walk through” their facilities and receive real-time AI insights overlaid on their view.
Conclusion
AI-driven innovation is fundamentally transforming cannabis cultivation from an artisanal craft into a data-driven science without losing the nuance and care that produce exceptional products. The technology enables unprecedented precision, efficiency, and consistency while addressing the unique challenges of this highly regulated, rapidly evolving industry.
For cultivators willing to embrace these tools, the advantages are compelling: higher yields, better quality, lower costs, and reduced environmental impact. As the technology matures and becomes more accessible, we’ll likely see AI adoption accelerate across
operations of all sizes.
Yet technology alone isn’t a panacea. The most successful implementations combine AI’s analytical power with human expertise and intuition. The future of cannabis farming lies not in replacing growers with algorithms but in empowering cultivators with unprecedented insight into their crops, allowing them to make better decisions faster and grow exceptional cannabis more reliably than ever before.
As we stand at this intersection of agriculture and artificial intelligence, one thing seems certain: the cannabis farms of tomorrow will look radically different from those of today, driven by innovations that are only beginning to reveal their full potential.




